1.无状态登录原理
1.1.什么是有状态?
有状态服务,即服务端需要记录每次会话的客户端信息,从而识别客户端身份,根据用户身份进行请求的处理,典型的设计如tomcat中的session。
例如登录:用户登录后,我们把登录者的信息保1存在服务端session中,并且给用户一个cookie值,记录对应的session。然后下次请求,用户携带cookie值来,我们就能识别到对应session,从而找到用户的信息。
缺点是什么?
- 服务端保存大量数据,增加服务端压力
- 服务端保存用户状态,无法进行水平扩展
- 客户端请求依赖服务端,多次请求必须访问同一台服务器
1.2.什么是无状态
微服务集群中的每个服务,对外提供的都是Rest风格的接口。而Rest风格的一个最重要的规范就是:服务的无状态性,即:
- 服务端不保存任何客户端请求者信息
- 客户端的每次请求必须具备
自描述信息,通过这些信息识别客户端身份
带来的好处是什么呢?
- 客户端请求不依赖服务端的信息,任何多次请求不需要必须访问到同一台服务
- 服务端的集群和状态对客户端透明
- 服务端可以任意的迁移和伸缩
- 减小服务端存储压力
1.3.如何实现无状态
无状态登录的流程:
- 当客户端第一次请求服务时,服务端对用户进行信息认证(登录)
- 认证通过,将用户信息进行加密形成token,返回给客户端,作为登录凭证
- 以后每次请求,客户端都携带认证的token
- 服务端对token进行解密,判断是否有效。
流程图:
整个登录过程中,最关键的点是什么?
token的安全性
token是识别客户端身份的唯一标示,如果加密不够严密,被人伪造那就完蛋了。
采用何种方式加密才是安全可靠的呢?
我们将采用JWT来生成token,保证token的安全性
1.4.JWT
1.4.1.简介
JWT,全称是Json Web Token, 是JSON风格轻量级的授权和身份认证规范,可实现无状态、分布式的Web应用授权;官网:https://jwt.io

GitHub上jwt的java客户端:https://github.com/jwtk/jjwt
1.4.2.数据格式
JWT包含三部分数据:
Header:头部,通常头部有两部分信息:
我们会对头部进行base64加密(可解密),得到第一部分数据
Payload:载荷,就是有效数据,一般包含下面信息:
- 标准载荷:JWT规定的信息,jwt的元数据:
- JTI: JWT的id,当前jwt的唯一标识(像身份证号)
- IAT: issue at 签发时间
- EXP:过期时间
- SUB:签发人
- …
- 自定义载荷:
- 用户身份信息,(注意,这里因为采用base64加密,可解密,因此不要存放敏感信息)
这部分也会采用base64加密,得到第二部分数据
Signature:签名,是整个数据的认证信息。一般根据前两步的数据,再加上服务的的密钥(secret)(不要泄漏,最好周期性更换),通过加密算法生成。用于验证整个数据完整和可靠性
生成的数据格式:

可以看到分为3段,每段就是上面的一部分数据
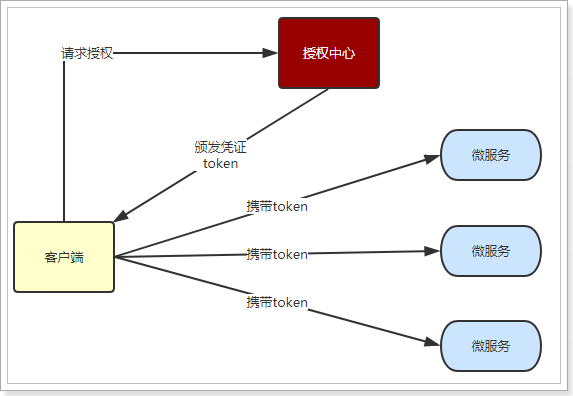
1.5.JWT登录流程
登录一般包含授权、鉴权两部分:
流程图如下:

- 授权流程authorize:
- 1、用户请求登录,携带用户名密码到
授权中心 - 2、
授权中心携带用户名密码,到用户中心查询用户 - 3、查询如果正确,
生成JWT凭证 - 4、把JWT写入用户cookie
- 鉴权流程authenticate:
- 1、用户请求某微服务功能,携带JWT
- 2、微服务验证JWT是否有效
- 3、微服务判断校验结果,成功或失败
- 4、失败则直接返回401
- 5、成功则处理业务并返回
因为JWT签发的token中已经包含了用户的身份信息,并且每次请求都会携带,这样服务的就无需保存用户信息,甚至无需去数据库查询,完全符合了Rest的无状态规范。
2.编写JWT工具
因为生成jwt,解析jwt这样的行为以后在其它微服务中也会用到,因此我们会抽取成工具,放到ly-auth-pojo中。
我们会用到比较流行的java语言的JWT工具,jjwt,官网如下:
2.1.依赖
我们需要先在ly-auth-pojo中引入JWT依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| <dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-api</artifactId>
<version>0.11.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-impl</artifactId>
<version>0.11.2</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-jackson</artifactId>
<version>0.11.2</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-time</groupId>
<artifactId>joda-time</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
2.2.载荷对象
JWT中,会保存载荷数据,我们计划存储2部分:
- jti:jwt的id
- UserDetail:用户数据
为了方便后期获取,我们定义一个类来封装。
我们在ly-auth-pojo中的com.leyou.auth.dto包下添加一个实体类,代表载荷信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| package com.leyou.auth.dto;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Payload {
private String jti;
private UserDetail userDetail;
}
|
载荷中的userInfo信息,也需要一个实体类表示,这里我们定义一个UserDetail类。
这里我们假设用户信息包含2部分:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| package com.leyou.auth.dto;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor(staticName = "of")
@NoArgsConstructor
public class UserDetail {
private Long id;
private String username;
}
|
2.3.工具
我们在ly-auth-pojo中的com.leyou.auth.utils包下创建一个工具类,用来封装几个方法:
- createJwt() :生成JWT
- parseJwt() :验证并解析JWT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
| package com.leyou.auth.utils;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.leyou.auth.dto.Payload;
import com.leyou.auth.dto.UserDetail;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Claims;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jws;
import io.jsonwebtoken.JwtParser;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts;
import io.jsonwebtoken.security.Keys;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.joda.time.DateTime;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.UUID;
public class JwtUtils {
private final JwtParser jwtParser;
private final SecretKey secretKey;
private final static ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
public JwtUtils(String key) {
secretKey = Keys.hmacShaKeyFor(key.getBytes(Charset.forName("UTF-8")));
this.jwtParser = Jwts.parserBuilder().setSigningKey(secretKey).build();
}
public String createJwt(Object userDetails) {
return createJwt(userDetails, 1800);
}
public String createJwt(Object userDetails, int expireSeconds) {
try {
return Jwts.builder().signWith(secretKey)
.setId(createJti())
.claim("user", mapper.writeValueAsString(userDetails))
.setExpiration(DateTime.now().plusSeconds(expireSeconds).toDate())
.compact();
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public Payload parseJwt(String jwt) {
try {
Jws<Claims> claimsJws = jwtParser.parseClaimsJws(jwt);
Claims claims = claimsJws.getBody();
Payload payload = new Payload();
payload.setJti(claims.getId());
payload.setUserDetail(mapper.readValue(claims.get("user", String.class), UserDetail.class));
return payload;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private String createJti() {
return StringUtils.replace(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), "-", "");
}
}
|
2.4.测试
我们在ly-auth-service中测试刚刚写的工具.
2.4.1.引入依赖
我们在ly-auth-service中引入ly-auth-pojo的依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<dependency>
<groupId>com.leyou</groupId>
<artifactId>ly-auth-pojo</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
|
2.4.2.配置秘钥
然后在ly-auth-service的application.yml文件中配置秘钥:
1
2
3
| ly:
jwt:
key: helloWorldJavaLeyouAuthServiceSecretKey
|
然后,我们在ly-auth-service的com.leyou.auth.config中定义一个配置类,注册JwtUtils注入到Spring的容器。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| package com.leyou.auth.config;
import com.leyou.auth.utils.JwtUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class JwtConfig {
@Value("${ly.jwt.key}")
private String key;
@Bean
public JwtUtils jwtUtils(){
return new JwtUtils(key);
}
}
|
2.4.3.测试类
然后在ly-auth-service中定义一个测试类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| package com.leyou.auth.test;
import com.leyou.auth.dto.Payload;
import com.leyou.auth.dto.UserDetail;
import com.leyou.auth.utils.JwtUtils;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class JwtTest {
@Autowired
private JwtUtils jwtUtils;
@Test
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
String jwt = jwtUtils.createJwt(UserDetail.of(1L, "Jack"));
System.out.println("jwt = " + jwt);
Payload payload = jwtUtils.parseJwt(jwt);
System.out.println("payload = " + payload);
}
}
|
结果:
1
2
3
4
| jwt = eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiIzZTg1NWVlYmFiN2I0NDM1YjY2NzFiMzhmNDcwM2E5ZSIsInVzZXIiOiJ7XCJpZFwiOjEsXCJ1c2VybmFtZVwiOlwiSmFja1wifSJ9.gnedpS9LE0VjetKVTyD2Opvi4eSyROOG_rSwQP0kDC0
payload = Payload)
|
3.登录授权
首先,我们来完成登录授权功能。这个功能要在我们的ly-auth-service项目中完成。
3.1.思路分析
在登录页面,用户会填写账号密码并提交,我们服务端接收后需要验证用户名和密码。如果验证通过则生成JWT并写入cookie中。不过验证用户名和密码需要去访问ly-user才可以,因此整体思路如下:
- 用户提交用户名和密码到ly-auth
- ly-auth远程访问ly-user,根据用户名和密码查询用户
- ly-auth验证查询结果
- 如果成功,生成jwt,并将JWT写入cookie
- 如果失败,返回401
3.2.用户验证的接口
用户中心ly-user必须对外提供查询接口,方便ly-auth做用户名密码校验。
3.2.1.定义接口
首先在ly-user-api定义接口:
引入依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-openfeign-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.leyou</groupId>
<artifactId>ly-user-pojo</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
|
在ly-user-api的com.leyou.user.client中,添加接口:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| package com.leyou.user.client;
import com.leyou.user.dto.UserDTO;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@FeignClient("user-service")
public interface UserClient {
@GetMapping("info")
UserDTO queryUserByUsernameAndPassword(@RequestParam("username") String username, @RequestParam("password") String password);
}
|
3.2.2.ly-auth引用接口
然后,在ly-auth-service中引入ly-user-interface和feign的依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.leyou</groupId>
<artifactId>ly-user-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
|
然后在ly-auth的com.leyou.auth包下的启动类LyAuthApplication上添加注解:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| package com.leyou.auth;
import com.leyou.auth.config.JwtProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages = "com.leyou.user.client")
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = {"com.leyou.auth", "com.leyou.common.advice"})
public class LyAuthApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(LyAuthApplication.class, args);
}
}
|
注意:对FeignClient的扫描包要添加到@EnableFeignClients注解里面!
3.3.登录的controller
接下来,我们需要在ly-auth-service编写一个接口,对外提供登录授权服务,接收用户名和密码,生成JWT。
我们在ly-auth的com.leyou.auth.web下添加UserAuthController,并编写登录接口:
- 请求方式:post
- 请求路径:/user/login
- 请求参数:username和password,另外写cookie要用到HttpServletResponse
- 返回结果:无,直接写入cookie
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| package com.leyou.auth.web;
import com.leyou.auth.service.UserAuthService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserAuthController {
@Autowired
private UserAuthService userAuthService;
@PostMapping("login")
public ResponseEntity<Void> login(
@RequestParam("username") String username,
@RequestParam("password") String password,
HttpServletResponse response){
userAuthService.login(username, password, response);
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
}
}
|
3.4.登录的service
service的基本流程:
- 去ly-user查询用户
- 判断用户结果,正确则生成jwt
- 把jwt写入cookie
这里还有几个属性要配置,包括:
- cookie名称
- cookie的domain属性,决定cookie在哪些域名下生效
这三个属性我们定义到一个常量类中,放到ly-auth-pojo下的 com.leyou.auth.constants中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| package com.leyou.auth.constants;
public class JwtConstants {
public static final String COOKIE_NAME = "LY_TOKEN";
public static final String DOMAIN = "leyou.com";
}
|
注意:cookie的domain决定了cookie作用的域名,写成”leyou.com“可以让leyou.com下的所有二级以上域名共享cookie
在ly-auth-service的com.leyou.auth.service包中定义接口:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| package com.leyou.auth.service;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public interface UserAuthService {
void login(String username, String password, HttpServletResponse response);
}
|
在ly-auth-service的com.leyou.auth.service.impl包中定义实现类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| package com.leyou.auth.service.impl;
import com.leyou.auth.dto.UserDetail;
import com.leyou.auth.service.UserAuthService;
import com.leyou.auth.utils.JwtUtils;
import com.leyou.auth.constants.JwtConstants;
import com.leyou.common.exception.LyException;
import com.leyou.user.client.UserClient;
import com.leyou.user.dto.UserDTO;
import feign.FeignException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@Service
public class UserAuthServiceImpl implements UserAuthService {
private final UserClient userClient;
private final JwtUtils jwtUtils;
public UserAuthServiceImpl(UserClient userClient, JwtUtils jwtUtils) {
this.userClient = userClient;
this.jwtUtils = jwtUtils;
}
@Override
public void login(String username, String password, HttpServletResponse response) {
try {
UserDTO user = userClient.queryUserByUsernameAndPassword(username, password);
if (user == null) {
throw new LyException(400, "用户名或密码错误!");
}
UserDetail userDetails = UserDetail.of(user.getId(), user.getUsername());
String jwt = jwtUtils.createJwt(userDetails);
writeCookie(response, jwt);
} catch (FeignException e) {
throw new LyException(e.status(), e.contentUTF8());
}
}
private void writeCookie(HttpServletResponse response, String token) {
Cookie cookie = new Cookie(JwtConstants.COOKIE_NAME, token);
cookie.setDomain(JwtConstants.DOMAIN);
cookie.setHttpOnly(true);
cookie.setMaxAge(-1);
cookie.setPath("/");
response.addCookie(cookie);
}
}
|
3.5.测试
在登录页面填写信息,登录后跳转到首页,发现token成功写入了:

4.秘钥管理
用户访问微服务的时候会携带JWT,而微服务中需要对JWT做校验和解析,这个时候就会用到秘钥。
但是秘钥保存在ly-auth这个授权服务中,我们不能随意暴露秘钥,否则就会有秘钥泄露的风险。
那么,该如何管理秘钥,让我们的微服务安全获取秘钥呢?
4.1.思路分析
微服务要想安全获取秘钥,必须经过ly-auth的身份验证。因此,我们可以给每一个微服务都定义一份“身份信息”,这些身份信息保存在数据库中,结构如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for tb_client_info
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `tb_client_info`;
CREATE TABLE `tb_client_info` (
`id` int(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`client_id` varchar(32) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '服务名称',
`secret` varchar(60) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '密钥',
`info` varchar(128) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '服务介绍',
`create_time` timestamp(0) NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(0) COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` timestamp(0) NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(0) ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(0) COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE,
UNIQUE INDEX `uq_key_service_name`(`client_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 10 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci COMMENT = '服务信息表,记录微服务的id,名称,密文,用来做服务认证' ROW_FORMAT = Compact;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of tb_client_info
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `tb_client_info` VALUES (1, 'user-service', '$2a$10$LjOQwjNv.4cO0uftZkvZzOfhpXQxqU.XrHL5Ut6m3G4OXBkQQQdBe', '用户微服务', '2019-04-10 15:55:11', '2020-06-14 21:12:16');
INSERT INTO `tb_client_info` VALUES (2, 'item-service', '$2a$10$LjOQwjNv.4cO0uftZkvZzOfhpXQxqU.XrHL5Ut6m3G4OXBkQQQdBe', '商品微服务', '2019-04-10 15:55:11', '2020-06-14 21:12:17');
INSERT INTO `tb_client_info` VALUES (3, 'page-service', '$2a$10$LjOQwjNv.4cO0uftZkvZzOfhpXQxqU.XrHL5Ut6m3G4OXBkQQQdBe', '静态页微服务', '2019-04-10 15:55:11', '2020-06-14 21:12:18');
INSERT INTO `tb_client_info` VALUES (4, 'search-service', '$2a$10$LjOQwjNv.4cO0uftZkvZzOfhpXQxqU.XrHL5Ut6m3G4OXBkQQQdBe', '搜索微服务', '2019-04-10 15:55:11', '2020-06-14 21:12:19');
INSERT INTO `tb_client_info` VALUES (5, 'cart-service', '$2a$10$LjOQwjNv.4cO0uftZkvZzOfhpXQxqU.XrHL5Ut6m3G4OXBkQQQdBe', '购物车微服务', '2019-04-10 15:55:11', '2020-06-14 21:12:20');
INSERT INTO `tb_client_info` VALUES (6, 'trade-service', '$2a$10$LjOQwjNv.4cO0uftZkvZzOfhpXQxqU.XrHL5Ut6m3G4OXBkQQQdBe', '订单微服务', '2019-04-10 15:55:11', '2020-06-14 21:12:20');
INSERT INTO `tb_client_info` VALUES (7, 'api-gateway', '$2a$10$LjOQwjNv.4cO0uftZkvZzOfhpXQxqU.XrHL5Ut6m3G4OXBkQQQdBe', '网关服务', '2019-04-10 15:55:11', '2020-06-14 21:12:21');
INSERT INTO `tb_client_info` VALUES (8, 'auth-service', '$2a$10$LjOQwjNv.4cO0uftZkvZzOfhpXQxqU.XrHL5Ut6m3G4OXBkQQQdBe', '授权服务', '2019-04-10 15:55:11', '2020-06-14 21:12:22');
INSERT INTO `tb_client_info` VALUES (9, 'pay-service', '$2a$10$LjOQwjNv.4cO0uftZkvZzOfhpXQxqU.XrHL5Ut6m3G4OXBkQQQdBe', '支付微服务', '2019-04-10 15:56:38', '2020-06-14 21:12:24');
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
|
核心字段介绍:
- clientId:微服务的客户端id,每个微服务都有唯一id
- secret:客户端秘钥(密码),微服务身份验证会用到
一旦微服务有了身份,那么微服务申请秘钥的时候,ly-auth就可以对身份做验证,验证通过才发放秘钥,否则拿不到秘钥,流程如下:

微服务申请秘钥流程:
- 1.服务启动时向ly-auth申请秘钥,携带配置好的clientId和secret
- 2.ly-auth接收请求,根据clientId去数据库查询
- 3.验证clientId和secret
- 4.如果验证通过,则返回秘钥
我们需要做的准备包括:
- 在ly-auth服务中提供一个接口,微服务调用时可以获取秘钥
- 微服务启动后,向ly-auth发送请求,获取秘钥
4.2.基本代码
首先是client信息表相关的基本代码,包括实体类、mapper、service等。
4.2.1.引入依赖
既然要访问数据库,需要在ly-auth-service中引入数据库访问所需要的依赖。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
4.2.2.配置文件
然后是在ly-auth-service的yaml文件中添加数据库配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://ly-mysql:3306/heima?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&allowMultiQueries=true&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: auto
insert-strategy: not_null
update-strategy: not_null
type-aliases-package: com.leyou.auth.entity
|
4.2.3.实体类
首先在ly-auth-service的com.leyou.auth.entity包中添加实体类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| package com.leyou.auth.entity;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import com.leyou.common.entity.BaseEntity;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@TableName("tb_client_info")
public class ClientInfo extends BaseEntity {
@TableId
private Long id;
private String clientId;
private String secret;
private String info;
}
|
4.2.4.mapper
在ly-auth-service的com.leyou.auth.mapper包中添加mapper接口:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| package com.leyou.auth.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.leyou.auth.entity.ClientInfo;
public interface ClientMapper extends BaseMapper<ClientInfo> {
}
|
4.2.5.service
在ly-auth-service的com.leyou.auth.service包中添加接口:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| package com.leyou.auth.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.leyou.auth.entity.ClientInfo;
public interface ClientService extends IService<ClientInfo> {
}
|
在ly-auth-service的com.leyou.auth.service.impl包中添加接口实现类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| package com.leyou.auth.service.impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.leyou.auth.entity.ClientInfo;
import com.leyou.auth.mapper.ClientMapper;
import com.leyou.auth.service.ClientService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class ClientServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ClientMapper, ClientInfo> implements ClientService {
}
|
4.2.6.扫描包
在ly-auth-service的启动类上添加注解,完成mapper扫描:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| package com.leyou.auth;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
@MapperScan("com.leyou.auth.mapper")
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages = "com.leyou.user.client")
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = {"com.leyou.auth", "com.leyou.common.advice"})
public class LyAuthApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(LyAuthApplication.class, args);
}
}
|
4.2.7.密码加密
数据库中的密码加密采用的是Bcrypt算法,这里也需要配置加密工具。
我们在ly-auth-service的com.leyou.auth.config包的JwtConfig中添加一个新的bean:
1
2
3
4
| @Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
|
4.3.申请秘钥的接口
我们在ly-auth中提供一个接口,提供给微服务调用,获取秘钥。
4.2.1.定义接口
在ly-auth-api中定义一个接口,格式如下:
- 请求方式:Get
- 请求路径:/client/key
- 请求参数:
- clientId:微服务id
- secret:微服务秘钥
- 返回值:秘钥对象,SecretKey
在ly-auth-api的pom文件中引入feign依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-openfeign-core</artifactId>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.leyou</groupId>
<artifactId>ly-auth-pojo</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
|
在com.leyou.auth.client包中定义接口:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| package com.leyou.auth.client;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@FeignClient("auth-service")
public interface AuthClient {
@GetMapping("/client/key")
String getSecretKey(@RequestParam("clientId") String clientId,@RequestParam("secret") String secret);
}
|
4.2.2.controller
在ly-auth-service的com.leyou.auth.web包中定义controller,实现接口:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| package com.leyou.auth.web;
import com.leyou.auth.service.ClientService;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("client")
public class ClientController {
private final ClientService clientService;
public ClientController(ClientService clientService) {
this.clientService = clientService;
}
@GetMapping("key")
public ResponseEntity<String> getSecretKey(@RequestParam("clientId") String clientId, @RequestParam("secret") String secret){
return ResponseEntity.ok(clientService.getSecretKey(clientId, secret));
}
}
|
4.2.3.Service
在ly-auth-service的com.leyou.auth.service包中添加接口:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| package com.leyou.auth.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.leyou.auth.entity.ClientInfo;
public interface ClientService extends IService<ClientInfo> {
String getSecretKey(String clientId, String secret);
}
|
在ly-auth-service的com.leyou.auth.service.impl包中添加接口实现类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| package com.leyou.auth.service.impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.leyou.auth.entity.ClientInfo;
import com.leyou.auth.mapper.ClientMapper;
import com.leyou.auth.service.ClientService;
import com.leyou.common.exceptions.LyException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class ClientServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ClientMapper, ClientInfo> implements ClientService {
private final PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Value("${ly.jwt.key}")
private String key;
public ClientServiceImpl(PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder) {
this.passwordEncoder = passwordEncoder;
}
@Override
public String getSecretKey(String clientId, String secret) {
ClientInfo client = query().eq("client_id", clientId).one();
if (client == null) {
throw new LyException(401, "客户端的信息有误," + clientId + "不存在!");
}
if (!passwordEncoder.matches(secret, client.getSecret())) {
throw new LyException(401, "客户端的信息有误,secret不正确!");
}
return key;
}
}
|
4.4.申请秘钥
我们把申请秘钥的功能写到ly-auth-api中,供其它微服务使用。其它微服务引入该依赖后,就会根据配置的clientId和secret,自动向ly-auth发起请求,申请秘钥。
我们约定微服务要在application.yml中配置自己的clientId和secret,格式如下:
1
2
3
4
| ly:
auth:
clientId: xxx
secret: xxx
|
因此我们要在ly-auth-api的com.leyou.auth.config包中定义一个属性类,读取这两个属性。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| package com.leyou.auth.config;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties("ly.auth")
public class ClientProperties {
private String clientId;
private String secret;
}
|
另外,我们需要在读取到clientId和secret以后,向ly-auth发出请求,申请秘钥,因此我们在ly-auth-api中定义一个配置类,完成秘钥加载,并完成对JwtUtils的初始化:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| package com.leyou.auth.config;
import com.leyou.auth.client.AuthClient;
import com.leyou.auth.utils.JwtUtils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
@Slf4j
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "ly.auth", name = {"clientId", "secret"})
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ClientProperties.class)
public class AuthConfiguration {
private AuthClient authClient;
private ClientProperties properties;
public AuthConfiguration(AuthClient authClient, ClientProperties properties) {
this.authClient = authClient;
this.properties = properties;
}
@Bean
@Primary
public JwtUtils jwtUtils(){
try {
String key = authClient.getSecretKey(properties.getClientId(), properties.getSecret());
JwtUtils jwtUtils = new JwtUtils(key);
log.info("秘钥加载成功。");
return jwtUtils;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("初始化JwtUtils失败,{}", e.getMessage());
throw e;
}
}
}
|
注意,在配置类上的一个条件值的关注:
1
| @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "ly.auth", name = {"clientId", "secret"})
|
条件注解,意思是环境中必须有ly.auth开头的属性,属性名称必须叫clientId和secret,确保使用者会在yml中配置clientId和secret时,当前配置才会生效。
还有这个:
1
| @EnableFeignClients(basePackages = "com.leyou.auth.client")
|
目的是引入刚刚编写的AuthClient,方便查询秘钥
最后,为了让这个配置被SpringBoot加载,我们需要在ly-auth-api的resources目录中创建一个文件夹:META-INF,然后创建一个文件:spring.factories,然后填写内容:
1
| org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.leyou.auth.config.AuthConfiguration
|
如图:

另外,这样用户写yaml时是没有提示的,为了有提示,需要在META-INF下新建一个文件:spring-configuration-metadata.json,内容如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| {
"groups": [
{
"name": "ly.auth",
"type": "com.leyou.auth.config.ClientProperties",
"sourceType": "com.leyou.auth.config.ClientProperties"
}
],
"properties": [
{
"name": "ly.auth.clientId",
"type": "java.lang.String",
"sourceType": "com.leyou.auth.config.ClientProperties",
"description": "授权客户端的id"
},
{
"name": "ly.auth.secret",
"type": "java.lang.String",
"sourceType": "com.leyou.auth.config.ClientProperties",
"description": "授权客户端的secret"
},
{
"name": "ly.auth.includeFilterPaths",
"type": "java.lang.String",
"sourceType": "com.leyou.auth.config.ClientProperties",
"description": "登录拦截要包含的路径"
},
{
"name": "ly.auth.secret",
"type": "java.lang.excludeFilterPaths",
"sourceType": "com.leyou.auth.config.ClientProperties",
"description": "登录拦截放行的路径"
}
],
"hints": []
}
|
4.5.测试
我们在ly-user中测试下这个功能。
首先,在ly-user-service中引入相关依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
<dependency>
<groupId>com.leyou</groupId>
<artifactId>ly-auth-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
接着,在ly-user-service的application.yml中配置客户端信息:
1
2
3
4
5
| ly:
auth:
clientId: user-service
secret: 1234
|
修改启动类,添加注解:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| # ...
@EnableFeignClients
public class LyUserApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(LyUserApplication.class);
}
}
|
重启ly-user-service,应该能看到日志输出:
1
| 2030-06-20 08:29:26.519 INFO 12232 --- [ main] com.leyou.auth.config.AuthConfig : 秘钥加载成功。
|
5.登录验证
用户登录后,会携带JWT访问微服务,而微服务需要验证当前访问者的身份,如果验证通过则执行后续业务,验证失败,则拦截请求:

很多微服务都需要做用户登录状态验证,因此我们可以把这部分拦截和判断写到ly-auth-api中,作为工具。
5.1.登录拦截器
在ly-auth-api引入编写拦截器所需依赖:
注意: <optional>true</optional>一定要配置, 因为待会要在Gateway网关中引用它, 而网关使用的是WebFlux这是异步的, 它和WebMVC有冲突, 所以只能在本项目下使用它
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.leyou</groupId>
<artifactId>ly-common</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
|
在ly-auth-api的com.leyou.auth.interceptors中编写一个拦截器:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| package com.leyou.auth.interceptors;
import com.leyou.auth.constants.JwtConstants;
import com.leyou.auth.dto.Payload;
import com.leyou.auth.dto.UserDetail;
import com.leyou.auth.utils.JwtUtils;
import com.leyou.common.exception.LyException;
import com.leyou.common.utils.CookieUtils;
import io.jsonwebtoken.JwtException;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@Slf4j
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
private final JwtUtils jwtUtils;
public LoginInterceptor(JwtUtils jwtUtils) {
this.jwtUtils = jwtUtils;
}
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) {
try {
String jwt = CookieUtils.getCookieValue(request, JwtConstants.COOKIE_NAME);
Payload payload = jwtUtils.parseJwt(jwt);
UserDetail userDetail = payload.getUserDetail();
log.info("用户{}正在访问。", userDetail.getUsername());
return true;
} catch (JwtException e) {
throw new LyException(401, "JWT无效或过期!", e);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e){
throw new LyException(401, "用户未登录!", e);
}
}
}
|
5.2.配置拦截器
拦截器编写了还需要注册到SpringMVC中,因此我们编写配置类,完成拦截器注册。不过,拦截器的注册可能需要指定两个参数:
- 拦截路径:指定拦截器对哪些路径生效
- 放行路径:指定拦截器对哪些路径放行
我们约定用户会在application.yml中配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| ly:
auth:
clientId: user-service
secret: 1234
excludeFilterPaths:
- /aa/**
- /bb/**
includeFilterPaths:
- /xx/**
- /yy/**
|
因此,我们要在ClientProperties中添加两个属性,来读取其中的值:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| package com.leyou.auth.config;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import java.util.List;
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties("ly.auth")
public class ClientProperties {
private String clientId;
private String secret;
private List<String> includeFilterPaths;
private List<String> excludeFilterPaths;
}
|
然后在ly-auth-api中的com.leyou.auth.config包下编写一个配置类,配置拦截器:
注意: 一定要加@Lazy, 因为WbMvcConfigurer是在Web环境创建时运行, 而JwtUtils需要Web环境创建完之后再运行, 如果让WebMvcConfigurer依赖JwtUtils, 那就会产生冲突, 故而加上@Lazy注解
@Lazy: 可以理解为延迟加载, Spring会先给它个代理对象, 等要用到的时候代理对象就会从IOC容器中拿.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| package com.leyou.auth.config;
import com.leyou.auth.interceptors.LoginInterceptor;
import com.leyou.auth.utils.JwtUtils;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Lazy;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
public class MvcConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer {
private JwtUtils jwtUtils;
private ClientProperties properties;
public MvcConfiguration(@Lazy JwtUtils jwtUtils, ClientProperties properties) {
this.jwtUtils = jwtUtils;
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
InterceptorRegistration registration = registry.addInterceptor(new LoginInterceptor(jwtUtils));
if(!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(properties.getIncludeFilterPaths())){
registration.addPathPatterns(properties.getIncludeFilterPaths());
}
if(!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(properties.getExcludeFilterPaths())){
registration.excludePathPatterns(properties.getExcludeFilterPaths());
}
}
}
|
5.3.拦截器开关
我们通过自定义的MvcConfiguration向mvc中配置了拦截器,但是MvcConfiguration并没有被Spring扫描,因此配置并未生效。
要想让配置生效,必须得让spring扫描到MvcConfiguration这个类。
但是引用ly-auth-api的服务可能只是需要JwtUtils,不需要做登录拦截,因此我们需要定义一个开关,用来开启或关闭拦截器功能。
在ly-auth-api的com.leyou.auth.annotation包中定义一个注解:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| package com.leyou.auth.annotation;
import com.leyou.auth.config.MvcConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Import(MvcConfiguration.class)
@Documented
@Inherited
public @interface EnableJwtVerification {
}
|
这个注解通过@Import(MvcConfiguration.class)来加载MvcConfiguration类,因此任何项目只要引入了@EnableJwtVerification就可以使得MvcConfiguration生效,从而使拦截器生效。
5.4.测试
现在,我们在ly-user-service测试拦截器。
首先,在ly-user-service的启动类上,添加@EnableJwtVerification注解,开启登录拦截器功能:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| package com.leyou.user;
import com.leyou.auth.annotation.EnableJwtVerification;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
@EnableJwtVerification
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages = "com.leyou.auth.client")
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = {"com.leyou.user", "com.leyou.common.advice"})
@MapperScan("com.leyou.user.mapper")
public class LyUserApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(LyUserApplication.class,args);
}
}
|
然后在ly-user-service的com.leyou.user.web包中添加一个controller,方便测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| package com.leyou.user.web;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("address")
public class AddressController {
@GetMapping("hello")
public ResponseEntity<String> hello(){
return ResponseEntity.ok("上海浦东新区航头镇航头路18号传智播客");
}
}
|
然后在ly-user-service的application.yml中配置拦截和放行路径:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| ly:
auth:
clientId: user-service
secret: 1234
includeFilterPaths:
- /address/**
|
重启ly-user-service服务,浏览器中访问地址:

然后登录一下,再次访问:

6.页面获取用户信息
虽然cookie已经成功写入,但是我们首页的顶部,登录状态依然没能判断出用户信息:

我们思考一下,应该如何获取用户信息呢?
6.1.步骤分析
我们现在使用的是无状态登录,用户身份写入了jwt,解析JWT即可获取用户信息。但是jwt需要通过秘钥解析才知道是否有效,才可以解析用户身份。因此查询用户信息一定要发请求到服务端。
分析一下步骤:
- 1)页面向后台发起请求,携带cookie
- 2)后台获取cookie中的jwt
- 3)校验jwt是否有效
- 无效:登录失效或未登录,返回错误信息
- 有效:解析出里面的用户信息并返回
接下来,我们就分步实现上述功能。
6.2.页面JS代码
首先是页面发起请求,校验cookie。
页面的顶部已经被我们封装为一个独立的Vue组件,在/js/pages/shortcut.js中

打开js,发现里面已经定义好了Vue组件,并且在created函数中,查询用户信息:

因为jwt在cookie中,因此本次请求肯定会携带jwt信息在cookie中。
6.3.查询当前用户的接口
我们在ly-user-service中定义用户的校验接口,通过cookie获取jwt,然后校验通过返回用户信息。
- 请求方式:GET
- 请求路径:/info/me
- 请求参数:无,不过我们需要从cookie中获取jwt信息
- 返回结果:校验成功返回用户;校验失败,则返回401
在ly-user-service的com.leyou.user.web包的UserController中添加代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@GetMapping("me")
public ResponseEntity<UserDetail> me(){
return ResponseEntity.ok(null);
}
|
修改ly-user-service:的application.yml添加拦截路径,最新yml内容为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| server:
port: 8086
spring:
application:
name: user-service
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://ly-mysql:3306/heima?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&allowMultiQueries=true&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
redis:
host: ly-redis
rabbitmq:
host: ly-mq
username: leyou
password: 123321
virtual-host: /
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://ly-registry:10086/eureka
logging:
level:
com.leyou: debug
mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: auto
insert-strategy: not_null
update-strategy: not_null
type-aliases-package: com.leyou.user.entity
ly:
encoder:
crypt:
secret: ${random.uuid}
strength: 6
auth:
clientId: user-service
secret: 1234
includeFilterPaths:
- /address/**
- /info/me
|
6.4.用户上下文
现在,我们接收了用户的请求,但是该如何获取当前登录用户信息呢?
6.4.1.思路分析
其实,在ly-user-service中已经引入了ly-auth-api的依赖,而ly-auth-api中提供了一个拦截器LoginInterceptor,已经拦截请求并且获取了用户信息。
拦截器放行后才会进入UserController的方法me()中。那么,我们为什么不能把拦截器中获取的用户信息,保存起来,然后在UserController中直接获取并使用呢,如图:

步骤如下:
- 1.前端发出请求到服务端,查询登录用户信息
- 2.拦截器拦截请求,验证并解析JWT,得到用户信息UserDetails
- 3.将用户信息存入UserContext(需要自己实现)上下文,放行请求
- 4.controller处理请求,从UserContext获取用后,返回给前端
6.4.2.UserContext
UserContext用来存储当前的用户信息,但是该如何保存呢?
要知道用户的请求肯定是多线程并发访问的,如果直接将UserDetail存入UserContext的成员变量,会存在线程并发安全问题。我们必须保证每一个请求(一个线程)都有自己的用户信息,互不干扰!
1)ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal恰好满足这个需求,那么ThreadLocal是如何实现这一需求的呢?
看下这幅图:

关键点:
- 每个线程(
Thread)内部都持有一个ThreadLocalMap对象。 ThreadLocalMap的Key是某个ThreadLocal对象,值是任意Object。- 不同线程,内部有自己的
ThreadLocalMap,因此各线程资源互相不会干扰。
当我们使用ThreadLocal存储数据时,ThreadLocal会先得到当前线程(currentThread)对象,然后获取线程中的ThreadLocalMap对象,接着把数据存储到这个ThreadLocalMap对象中,因此每个线程的用户都在线程自己的ThreadLocalMap对象中,互不干扰。
2)UserContext
接下来,我们实现UserContext。在ly-auth-api中的com.leyou.auth.utils定义:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| package com.leyou.auth.utils;
import com.leyou.auth.dto.UserDetail;
public class UserContext {
private static final ThreadLocal<UserDetail> TL = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void setUser(UserDetail user) {
TL.set(user);
}
public static UserDetail getUser() {
return TL.get();
}
public static void removeUser() {
TL.remove();
}
}
|
6.4.3.存储用户
接下来,我们修改拦截器逻辑,获取用户后把用户存储在UserContext中。
修改ly-auth-api中的LoginInterceptor,完整代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| package com.leyou.auth.interceptors;
import com.leyou.auth.constants.JwtConstants;
import com.leyou.auth.dto.Payload;
import com.leyou.auth.dto.UserDetail;
import com.leyou.auth.dto.UserDetail;
import com.leyou.auth.utils.JwtUtils;
import com.leyou.auth.utils.UserContext;
import com.leyou.common.exception.LyException;
import com.leyou.common.utils.CookieUtils;
import io.jsonwebtoken.JwtException;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@Slf4j
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
private final JwtUtils jwtUtils;
public LoginInterceptor(JwtUtils jwtUtils) {
this.jwtUtils = jwtUtils;
}
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) {
try {
String jwt = CookieUtils.getCookieValue(request, JwtConstants.COOKIE_NAME);
Payload payload = jwtUtils.parseJwt(jwt);
UserDetail userDetails = payload.getUserDetail();
log.info("用户{}正在访问。", userDetails.getUsername());
UserContext.setUser(userDetails);
return true;
} catch (JwtException e) {
throw new LyException(401, "JWT无效或过期!", e);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e){
throw new LyException(401, "用户未登录!", e);
}
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {
UserContext.removeUser();
}
}
|
6.5.完成controller逻辑
现在,让我们补充完成ly-user-service中的UserController代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@GetMapping("me")
public ResponseEntity<UserDetails> me(){
return ResponseEntity.ok(UserContext.getUser());
}
|
6.6.测试
重启ly-auth-service后测试。
页面效果:















